
Why is the battery capacity decreasing? Why doesn't the old battery keep power anymore?
Your phone battery lasted a year ago in normal use for 24 hours, but nowadays not even half a day? The phone on the charge says it's charged, but after a while, the battery level is only 70%? Why should I pay attention to using the battery?
The purpose of this article is to familiarize yourself with the condition of the batteries and the issues associated with charging them, which, especially in the longer term, are of great importance for battery life. If you don't want to read the entire article, you'll find a summary of the issues discussed in the article at the end.
Let's start by studying the battery policy a little bit:
-
How does the battery generate power?
When talking about a battery, it means a set of two or more battery cells. Battery cells are usually packed inside a metal or plastic package. When a positive and negative pole is added to this packaging, we have a pack in our hands that already looks like a battery.
The battery cell generates electrical current by means of a chemical reaction. The more battery cells in the battery, the more power it can generate. But what is the chemical reaction that happens in the battery cell?
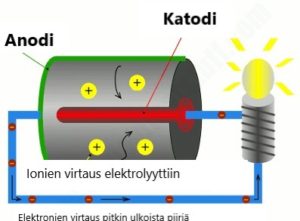 |
The main components of a single battery cell are a positive electrode, i.e. a cathode (in red), a negative electrode or anade (green), and a differentiating chemical called an electrolyte (in gray). When the cathode and the anode are combined with conductive material, such as a metal conductor (blue), chemical reactions begin to occur in the battery cell: one of these reactions produces electrons and positively charged ions in the anode. Positive ions flow into the electrolyte, while electrons flow through an external circuit (a wire connecting the anode and cathode) to the cathode.
If an electrically operated device, such as a lamp, is connected to an external circuit, the electrons will cause the lamp to ignite by flow ing along the external circuit. At the same time, another chemical reaction occurs in the cathode, in which the electrons entering it are combined with the ions.
The above process is called discharge of the battery. When the battery generates electrical current, the chemicals inside the battery cells gradually turn into other chemicals. As a result, the cell's ability to generate power fades, the cell's charge slowly decreases until over time the cell is powerless.
When the battery is charged, the operations that occur when discharged reverse: the electrons flow from caking to anode.
-
The battery performance of a two-year-old smartphone is just a shadow even more?
The battery's working principle is broadly the same regardless of the type of battery (lithium battery, nickel battery, lead-acid battery, etc.). Disassembling and charging the battery consumes it, which means that the battery will become unusable over time.
One way to measure battery durability is to look at how many charging cycles the battery lasts. For example, a typical lithium-ion battery lasts about 300-500 charge cycles depending on the use of the battery, as well as the stress of the battery. Since then, the battery is not yet unusable, but its maximum capacity has fallen to less than 80% of the original. This calculation cannot be prevented – but it can be accelerated by using the battery incorrectly.
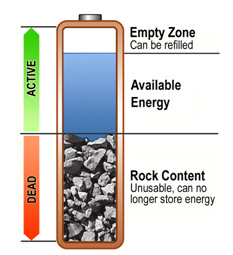
Let's take a look at the battery performance decrease with the following illustration. The picture shows a traditional battery, but you can think of it as any type of battery – the operating principle is the same.
In the photo, the battery is divided into an active and dead part.
The active part consists of the available energy, i.e. how much power the battery has. In addition, the active section may have an empty area that can be fully loaded. You should be concerned about the dead part of the battery: it cannot be recharging and does not store energy. In addition, it is a burden on the active part of the battery.
The battery's performance is slowly starting to decrease from the first day of the battery. As mentioned earlier, when the battery discharges, the chemicals contained in the battery cells become other chemicals. Fortunately, in most modern battery cells, self-discharge is minimal.
Discharge of lithium-ion batteries means, among other things, oxidation of the battery cell as part of normal use. When the battery is charged, it returns this reaction to the starting point – almost. Charging the battery returns the battery very close to its starting point, from which the battery was discharged. However, part of the chemical that has been transformed inside the battery cell remains in the changed state permanently, forming the cornerstone for the growth of the dead part.
Battery capacity decreases
In other words, when charging a new battery for the first time, the battery returns to 99.9% compared to its original state. Noteworthy is that the battery still shows 100% of the battery level. The next time the battery is charged, it will only charge 99.8% compared to its original state — when the battery still reports a 100% charge level. For this reason, especially for smartphones, it is worth remembering that the battery is a consumable – when the battery capacity and power are waning, it's time to buy a new battery, not necessarily a phone.
In addition to the above reason, the battery capacity can be reduced, for example, for lithium-ion batteries, maintaining the battery cell charge (storage) in violation of the manufacturer's instructions. The li-ion battery cell should charge more than 3.92V/cell (approx. 70% charged), or the electrolyte inside the battery cell begins to solidify, forming walls in front of the anode, preventing a reaction in the graphite anode.
This increases the internal resistance of the cell, accelerating battery wear. Therefore, do not empty the lithium battery! In fact, it is best to use the lithium-ion battery when it is 30% to 80%.
Maintaining the battery cell charge above 4.10V/cell or when the battery temperature is high, the electrolyte inside the battery cell is slowly oxidized in the cathode. This can lead to a sudden drop in capacity. Therefore, keeping the lithium-ion battery on continuous charging should be avoided. To charge lithium batteries, use a smart chargerthat identifies the needs of the battery.
If your battery has died, read the choice of new battery in our article: Best 18650 Battery? How to choose the right battery
-
What things should i keep in mind so that you don't impair battery performance by doing your own?
Maintaining battery performance does not involve black magic or nuclear physics, in fact, the battery behaves in many ways as humans do: it likes clean, light indoor work and constant, room temperature, but also works in varying conditions – for a shorter period of time.
When you're using a new battery, it's a good idea to be aware that it hasn't reached its full potential in terms of capacity – it only reaches it after a few charging cycles. This means that when a new battery comes in use, it usually has about 85% of its capacity, but after a few chargings it rises to 100% or at least very close to it.
Therefore, when using a new battery, it would be good – if possible, to load on ascent line: start using the battery with a small load, charge it, increase the load, reload. This is also called the battery run-in. Battery run-in applies to most battery types.
Lithium-ion battery manufacturers state that their batteries are at their full potential from the outset, but based on user-specific experience, the battery is available with low in-take power, especially if the battery has been stored for a long time.
Battery storage
When not using the battery, store it in a dry temperature of 15°C – 20°C. Do not allow the battery to freeze as it permanently damages the molecular structure of the molecules inside the battery cells. Charge and maintain the battery to be stored at 50-70% of its capacity, depending on the type of battery. This prevents the harmful battery from being deeply discharged, which occurs when the battery level drops below 2.5V.
When using the battery, attention should be paid to surrounding conditions – extreme conditions such as cold and hot are harmful to the battery. The battery's ability to generate power decreases with the temperature as chemical reactions slow down inside the battery cells. When you use your smartphone in the cold, your phone may suddenly report that the battery is low and turn off. However, your battery level does not fall dramatically from 70% to zero: due to slow-motion chemical reactions, your battery will not be able to generate enough power for your phone to continue to function, allowing your phone to interpret the battery as empty and shut down to protect your battery.
When the battery temperature rises due to load or external temperature, the resistance or resistance of chemical reactions inside the battery cells increases, reducing the battery voltage. To maintain the voltage, the battery would have to work more, which increases the battery temperature, increasing the resistance. That's how we have a treadmill ready. The result, however, the battery voltage drops rapidly, and the device on the battery will turn off when the voltage drops.
Charging

The battery is charged with different manufacturer's recommendations, depending on the type of battery. Some batteries, such as a lead-acid battery, are not picky for charging: if the voltage produced by the charger is appropriate, the battery may be in the charger for long periods of time without damaging the battery. However, nickel-based ( Ni-Cd , Ni-MH) batteries should not be kept charged in vain (this is the case when storing the battery).
The lithium-ion battery will not be damaged even if the battery is not fully charged and the charges are random. If the charger does not charge a single battery cell above 4.20V, the battery will not be damaged even if it is fully connected to the charger.
For lithium-ion and nickel batteries, so-called fast charging methods are available, charging the battery up to 50% in just 30 minutes. For fast charging, it is worth noting that while recovery in the battery cell is calm when charging, this step is accelerated in quick charging.
Fast charging risks that side reactions will occur in the process that reduce the battery condition. Therefore, "fast charge" and "ultra charge" are high-risk methods, which is why they should be avoided. These two should not be confused with the third, general method, "rapid charge", which is quite safe for the battery.
Check out our smart battery chargers for both li-ion batteries and rechargeable batteries: proakku .en/multi-function chargers/
-
Summary
- The battery generates power by chemical reactions. This consumes the battery, which means that the battery has its own life span.
- The battery consists of two or more battery cells. Inside the battery cell there is a positive electrode cathode, a negative electrode anode, and a chemical between them, an electrolyte.
- Battery life is measured on the charges it can withstand. For example, a typical lithium-ion battery lasts from 300 to 500 charge cycles before its capacity has fallen to less than 80% of the original. You won't be able to increase the number of charge cycles your battery offers, but with the right action, you can maximize the number of charge cycles. You can also use the wrong action to reduce the number of times you charge — a significant number.
- The battery can be divided into two parts when viewed, active and dead. The active part is a healthy battery, the dead part, in turn, a portion that is no longer able to be utilized and that takes up the capacity of the battery.
- To keep your battery running, consider the following:
- It's a good idea to drive the new battery in – start loading the battery with a light load and increase it with a scent, charge the battery when its charge level has fallen below 40%.
- Store the battery in a dry and about 15°C – 20°C and charge it to about 40-60%, depending on the type of battery. Monitor the battery level and charge if necessary.
- Avoid using and charging the battery when the battery is cold or hot. Keep in mind that the surrounding conditions also affect – in cold weather, the temperature of the battery also drops, while when it rises when hot, it rises.
- Find out how the battery manufacturer has instructed you to charge the battery type — with the wrong battery charge method, you can quickly ruin your battery.
- Choose a smart charger — get the most out of your batteries. Reliable Smart Chargers HERE
- Avoid "fast charge" and "ultra chrage" charging method. "Rapid charge" is the safest fast charge.
Remember that most batteries can get a new life by making a dosing! Check out our field and cost ing service HERE. If you need new 18650 batteries, read our article: How do I choose the right battery?
Proakku Jesse, the
Sources



Onko todellakin otsikon ”Miten akku tuottaa virtaa?” alla oleva toteamus paikkansapitävä : ”Mitä useampi akkukenno akussa on, sitä enemmän virtaa se pystyy tuottamaan.”?
Voisin kuvitella, että kennojen määrä vaikuttaa jännitteen suuruuteen, eikä virran suuruuteen. Jotenkin olen taipuvainen uskomaan, että virran suuruuteen vaikuttaa laite, joka purkaa akun varausta. Sen lisäksi kennojen koko vaikuttaa vain varauksen määrään – eli siihen, kuinka kauan laitteeseen riittää sen ottamaa virtaa.
Mutta on totta, että asiantuntijat voivat sanoa ja kirjoittaa monenlaista. Eräänkin sähköasentajan on kuultu asennuskohteessa huutaneen kollegoilleen kaapeli kädessään : ”Kulkeeko tässä kaapelissa jännite?” Yleensä jännite ei kulje mihinkään, mutta kun on tarpeeksi pätevä, voi tietysti laukoa mitä tahansa. Right?
metronidazole giardiasis
metronidazole giardiasis
preemptive gabapentin
preemptive gabapentin
remeron liquid
remeron liquid
is abilify a controlled substance
is abilify a controlled substance
protonix side effects long term use
protonix side effects long term use
why should you not take amitriptyline after 8pm?
why should you not take amitriptyline after 8pm?
actos perjudiciales
actos perjudiciales
acarbose ratiopharm
acarbose ratiopharm
does diltiazem cause hair loss
does diltiazem cause hair loss
ezetimibe formulation
ezetimibe formulation
how to get off effexor
how to get off effexor
robaxin methocarbamol
robaxin methocarbamol
repaglinide sulfonylurea
repaglinide sulfonylurea